Azure Synapse SQL DW Log Analytics Custom Metadata
Logging
There are two
versions of the custom logging scripts. One version for Azure Function and
another for Azure Automation. The steps to configure via Azure Function are
below. Azure automation is coming soon. Below are the links to the files:
Azure
Function Code Stack:
Azure Function Memory Collector GitHub
Azure Function Session Collector GitHub
Azure Function TempDB Collector
GitHub
Azure Function Resource Waits Collector GitHub
Azure Function Compute Waits Collector GitHub
Azure Function User Errors Collector GitHub
Azure Function Stored Procedure Collector GitHub
Azure Automation Code Stack:
Azure Automation Memory Collector GitHub
Azure Automation Session Collector GitHub
Azure Automation Tempdb Collector
GitHub
Azure Automation Resource Waits Collector GitHub
Azure Automation Compute Waits Collector GitHub
Azure Automation User Error Collector GitHub
Azure Automation Stored Procedure Collector GitHub
SQL Pool KQL
Examples:
Dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) KQLs GitHub
Newer Dedicated SQL pool Synapse Workspace KQLs GitHub
Enabling Logging for Azure Synapse:
First,
you can enable Azure log Analytics diagnostics monitoring for Azure Synapse in
the monitoring section of the blade.
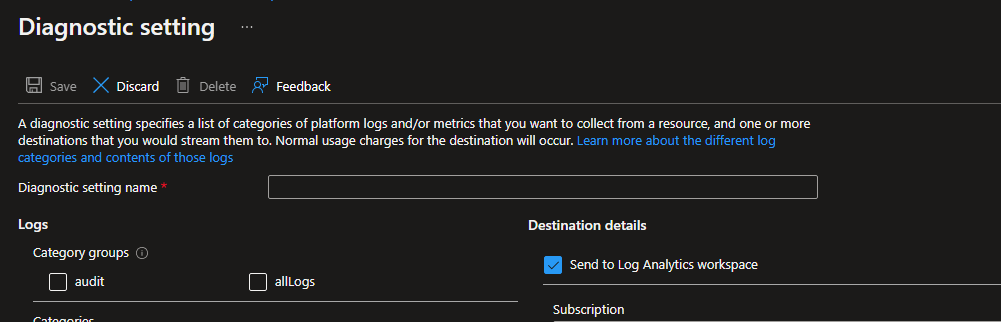
Finally,
select all the attributes to monitor and Azure Log Analytics destination.
Overview:
Steps:
Step
1:
The
steps below use an Azure Function using managed identity. If a SQL user
authentication is required, the script can be modified to use it. Please ensure
that any keys are stored in Azure Key Vault for additional security.
Create the Azure Function external user in Azure Synapse DW and provide the
view state permission as the below.
create user [function_name] from external provider;
GRANT VIEW DATABASE STATE TO [function_name]
Step
2:
Create
an Azure Function and copy the below script. Please ensure that all environment
variables are added to the configuration file $env:.
As you can see in the below script, the getdate
function is set to 30seconds prior, this interval can change to correlate with
the runtime of the function to ensure that only new data is being recorded.
# Input bindings are passed in
via param block.
param($Timer)
# Get the current universal time in the default
string format.
$currentUTCtime = (Get-Date).ToUniversalTime()
# The 'IsPastDue'
property is 'true' when the current function invocation is later than
scheduled.
if ($Timer.IsPastDue) {
Write-Host "PowerShell timer is running late!"
}
# Write an information log with the current time.
Write-Host "PowerShell timer trigger function ran! TIME: $currentUTCtime"
try {
###Context no longer needed as we will get the
Synapse SQL Pool instance name from the config parameter.###
### Set-AzContext -SubscriptionId $env:azpocsub
$SQLDW=@($env:AzureSynapse1);
##You can remove the below in Prod if you like
after testing#####
Write-Host $SQLDW
Write-Host $env:dwdb1
##Write-Host $env:azpocsub
################################################
###You can use a foreach loop if there are
multiple SQL DWs that require querying, you will have to set the instance and
DB for every foreach call###
###The below is using managed identity of the
Azure Function, ensure correct permissions is provided to the function in the
GRANT VIEW DATABASE STATE TO [functionnamehere]###
###Calls to synapse DW should not incur any
concurrency slots of resource usage when quiring DMVs###
$resourceURI = "https://database.windows.net/"
$tokenAuthURI = $env:MSI_ENDPOINT + "?resource=$resourceURI&api-version=2017-09-01"
$tokenResponse = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Get -Headers @{"Secret"="$env:MSI_SECRET"} -Uri $tokenAuthURI
$accessToken = $tokenResponse.access_token
$SqlConnection = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection
$SqlConnection.ConnectionString = "Server=tcp:$SQLDW,1433;Persist Security
Info=False;MultipleActiveResultSets=False;Encrypt=True;TrustServerCertificate=False;Initial
Catalog=$env:dwdb1;"
$SqlConnection.AccessToken = $AccessToken
$SqlCmd = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand
$SqlCmd.CommandText = "SELECT Count(1) AS TOTAL
`
from sys.dm_pdw_exec_sessions pwsess
join `
sys.dm_pdw_exec_requests pwrequ
`
on pwsess.session_id=pwrequ.session_id
`
where pwrequ.submit_time >=
DATEADD(second,-30,getdate()) `
AND pwrequ.session_id <> session_id()
"
$SqlCmd.Connection = $SqlConnection
$SqlAdapter = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlDataAdapter
$SqlAdapter.SelectCommand = $SqlCmd
$dataset = New-Object System.Data.DataSet
$SqlAdapter.Fill($dataset)
$SqlConnection.Close()
$SynapseSess=($DataSet.Tables[0]).TOTAL
if ($SynapseSess -ge 1)
{
# Replace with your Workspace ID From Log
Analytics
$CustomerId = $env:workspaceidsynapse1
# Replace with your Primary Key From Log Analytics
$SharedKey = $env:workspacekeysynapse
# Specify the name of the record type that you'll
be creating For This case it is Synapse Session info which will create a SynapseSessionDW table in the workspace to query
$LogType = "SynapseSessionDW"
# You can use an optional field to specify the
timestamp from the data. If the time field is not specified, Azure Monitor
assumes the time is the message ingestion time
$TimeStampField = ""
# The below metadata will be added to the
workspace if the condition is met. There is an initial check above before this
section executes to not waste resources
$resourceURI = "https://database.windows.net/"
$tokenAuthURI = $env:MSI_ENDPOINT + "?resource=$resourceURI&api-version=2017-09-01"
$tokenResponse = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Get -Headers @{"Secret"="$env:MSI_SECRET"} -Uri $tokenAuthURI
$accessToken = $tokenResponse.access_token
$SqlConnection = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection
$SqlConnection.ConnectionString = "Server=tcp:$SQLDW,1433;Persist Security
Info=False;MultipleActiveResultSets=False;Encrypt=True;TrustServerCertificate=False;Initial
Catalog=$env:dwdb1;"
$SqlConnection.AccessToken = $AccessToken
$SqlCmd = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand
$SqlCmd.CommandText = "select pwsess.session_id AS [Session_Id_s],
pwsess.status AS [Status_s],
pwsess.Login_Name, pwsess.Login_Time,
`
pwsess.Client_Id, pwsess.App_Name,
pwsess.Sql_Spid, pwrequ.Request_Id
AS [RequestId], pwrequ.Session_Id
AS [Session_id_r], `
pwrequ.status AS [Status_r],
pwrequ.start_time, pwrequ.end_time,
`
pwrequ.total_elapsed_time, pwrequ.Error_Id,
pwrequ.Command `
from sys.dm_pdw_exec_sessions pwsess
join `
sys.dm_pdw_exec_requests pwrequ
`
on pwsess.session_id=pwrequ.session_id
`
where pwrequ.submit_time >=
DATEADD(second,-30,getdate()) `
AND pwrequ.session_id <> session_id()
"
$SqlCmd.Connection = $SqlConnection
$SqlAdapter = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlDataAdapter
$SqlAdapter.SelectCommand = $SqlCmd
$dataset = New-Object System.Data.DataTable
$SqlAdapter.Fill($dataset)
$SqlConnection.Close()
###Convert the data to JSon
directly and select the specific objects needed from the above query, all
objects are selected in this case, but you can omit any if needed###
$SynapsePOC=$dataset | Select-Object Session_id_s, status_s,
login_name, login_time, client_id , app_name, sql_spid, RequestId, Session_id_r, status_r, start_time, end_time, total_elapsed_time, error_id,
command |ConvertTo-Json
# Create the function to create the authorization
signature
Function
Build-Signature ($customerId, $sharedKey, $date, $contentLength, $method, $contentType, $resource)
{
$xHeaders = "x-ms-date:" + $date
$stringToHash = $method + "`n" + $contentLength + "`n" + $contentType + "`n" + $xHeaders + "`n" + $resource
$bytesToHash = [Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes($stringToHash)
$keyBytes = [Convert]::FromBase64String($sharedKey)
$sha256 = New-Object
System.Security.Cryptography.HMACSHA256
$sha256.Key = $keyBytes
$calculatedHash = $sha256.ComputeHash($bytesToHash)
$encodedHash = [Convert]::ToBase64String($calculatedHash)
$authorization = 'SharedKey
{0}:{1}' -f $customerId,$encodedHash
return $authorization
}
# Create the function to create and post the
request
Function Post-LogAnalyticsData($customerId, $sharedKey, $body, $logType)
{
$method = "POST"
$contentType = "application/json"
$resource = "/api/logs"
$rfc1123date = [DateTime]::UtcNow.ToString("r")
$contentLength = $body.Length
$signature = Build-Signature `
-customerId $customerId `
-sharedKey $sharedKey `
-date $rfc1123date `
-contentLength $contentLength `
-method $method `
-contentType $contentType `
-resource $resource
$uri = "https://" + $customerId + ".ods.opinsights.azure.com" + $resource + "?api-version=2016-04-01"
$headers = @{
"Authorization" = $signature;
"Log-Type" = $logType;
"x-ms-date" = $rfc1123date;
"time-generated-field" = $TimeStampField;
}
$response = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $uri -Method $method -ContentType $contentType -Headers $headers -Body $body -UseBasicParsing
return $response.StatusCode
}
# Submit the data to the API endpoint
Post-LogAnalyticsData -customerId
$customerId -sharedKey $sharedKey -body ([System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes($SynapsePOC)) -logType $logType
}
} catch {
###########Catch Exception if there is an error###########
$Exception = $_.Exception.Message
###########Send Email of the exception###########
Write-Error
-Exception $Exception
} finally {
###########Close any potential open
connection###########
if ($SqlConnection.State -eq 'Open') {
$SqlConnection.Close()
}
}
Step
4:
The
first initial API call to Log analytics can take up to 10 minutes to create the
KQL table and load data. You can confirm that the table is created by checking
the Custom logs section of the Log Analytics workspace as the below. You can
still get an error message for up to 10 minutes until the table is created and
fully populated. After the subsequent API call, the insertion should be a lot
faster.
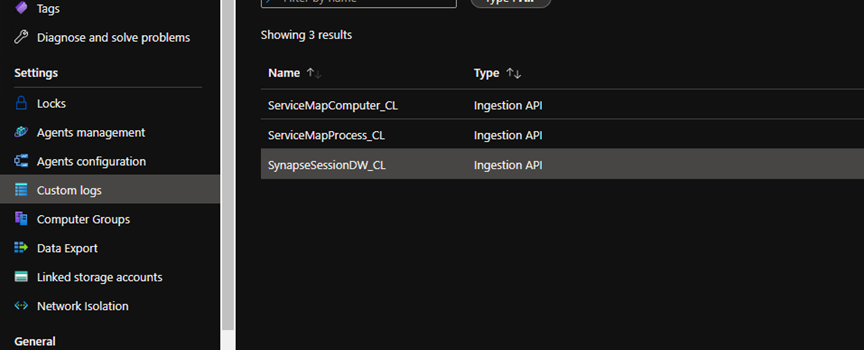
Please
note that you can delete the table if incorrect columns were created
or columns need to be adjusted by selecting the far right of the table.
Step
5:
You
can query the metadata by calling the SynapseSessionDW_CL
as the below. Please also note that the table name can be altered in the
script.
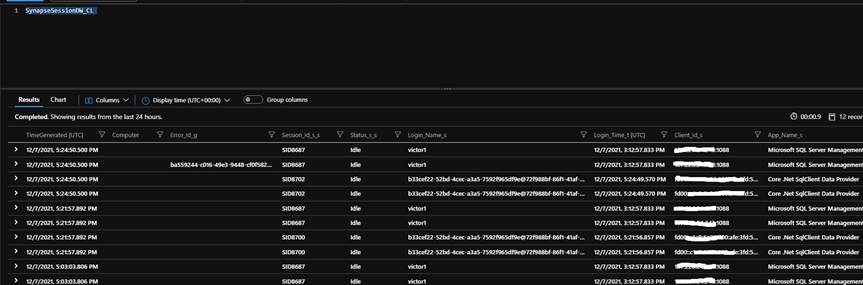
Step
6: Please note this is for the older SQL DW. Newer Syntax example coming soon.
For a great reference for additional KQLs for Azure Dedicated SQL
pools (formerly SQL DW) please visit the following link created by Nick Salch:
Azure
DW SQL POOL Log Analytics Queries GitHub
The full repo is located here:
Azure DW SQL Pool Full Repo GitHub
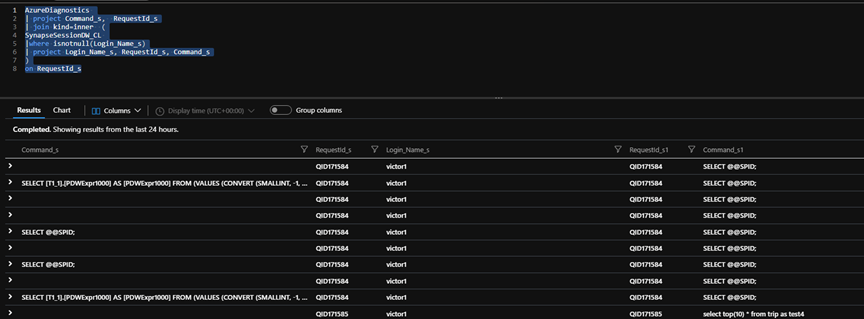
In
most cases you may want to add the data to an already created KQL table data
set. You can use something similar to the below to
join both tables. RequestId_s will be the required
join condition and column for each table.
Remember,
the Dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) and the Dedicated SQL pool created in
the Synapse workspace will have slightly different KQL tables to reference.
Please see below for more details.
let AzuresynapseDW
= 'synapseInstanceNameaHere';
AzureDiagnostics
| where Category == 'ExecRequests'
| where Resource == AzuresynapseDW
| where StatementType_s !in ('Batch','Execute')
| summarize TimeGenerated=max(TimeGenerated),
Start_Time=max(StartTime_t),
End_Time=max(EndTime_t),
Command=max(Command_s),
Last_Status=min(Status_s),
Statement_Type=max(StatementType_s),
Resource_class=max(ResourceClass_s)
by RequestId_s
| extend elapsedTime_min = (case(End_Time
=='1/1/1601, 12:00:00.000 AM', now(),End_Time) - case(Start_Time =='1/1/1601, 12:00:00.000 AM', now(),Start_Time ))/1m
| where elapsedTime_min > 1 | order by elapsedTime_min
desc | join kind=leftouter ( SynapseSessionDW_CL
|where isnotnull(Login_Name_s)
| project Login_Name_s, RequestId_s
)
on $left.RequestId_s==$right.RequestId_s
For more examples please visit:
Dedicated
SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) KQLs GitHub
Dedicated
SQL pool Synapse Workspace KQLs GitHub
DISCLAIMER: Sample Code is provided for the purpose of illustration only and is not intended to be used in a production environment unless thorough testing has been conducted by the app and database teams. THIS SAMPLE CODE AND ANY RELATED INFORMATION ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. We grant You a nonexclusive, royalty-free right to use and modify the Sample Code and to reproduce and distribute the object code form of the Sample Code, provided that. You agree: (i) to not use Our name, logo, or trademarks to market Your software product in which the Sample Code is embedded; (ii) to include a valid copyright notice on Your software product in which the Sample Code is embedded; and (iii) to indemnify, hold harmless, and defend Us and Our suppliers from and against any claims or lawsuits, including attorneys fees, that arise or result from the use or distribution or use of the Sample Code.